Biotin
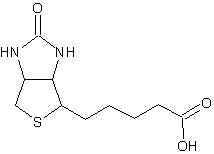
Figure 1. Biotin, C10H16N2O3S, Mw = 224,31 g/mol
Biotin occurs in foods as the free vitamin or bound to protein.
Synonyms for biotin:
- vitamin B7, co-enzyme R, vitamin H
Contents
- 1 Golden standard
- 2 Method indicator
- 3 Scope
- 4 Principle
- 5 Key steps
- 6 Remarks
- 7 Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- 8 Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
- 9 Proficiency testing schemes
- 10 Other methods available
- 11 Literature
- 12 EuroFIR assistance to this method/guidelines
Golden standard
EN 15607:2009 Foodstuffs - Determination of d-biotin by HPLC
Method indicator
- Name
- Code
Scope
The European Standard EN 15607 specifies a method for the determination of the mass fraction of d-biotin in foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). This method can also be used for estimation of d-biocytin, but it has to be noted that the method has not been validated for the determination of d-biocytin.
Principle
Pretreatments include enzymatic treatment followed by extraction. Quantification is done by HPLC with post-column binding reaction. Post-column reaction of d-biotin with avidin protein that is bound to a fluorescent marker, provides a specific method.
Key steps
Extraction
- The sample should be homogenised prior to extraction.
- Gluthatione solution, EDTA solution, citrate buffer solution and papain solution are added.
- Use of taka-diastase may be needed if the sample contains high amounts of starch.
- The sample solution is incubated overnight (37 °C).
- The solution is filtered.
HPLC
- Liquid chromatographic system consisting of a pump, an injector, a fluorescence detector (excitation wavelength 490 nm and emission wavelength 520 nm) and a data evaluation system.
- Reverse phase column: particle size 5 µm, diameter 4,0 mm, length 250 mm
- Mobile phase: phosphate buffer (pH 6):methanol (8:2, v:v)
- Also other chromatographic systems can be used if equivalent results are guaranteed.
- The performance criteria is the baseline separation of d-biotin from interferences.
- The system should include a post-column reactor derivatisation unit with a suitable reagent delivery system.
- d-biotin is derivatised with fluorescent avidin-fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate.
Identification and detection
- D-biotin is detected fluorometrically (excitation wavelength 490 nm, emission wavelength 520 nm)
- Identification of d-biotin is done by the comparison of the retention time obtained with the standard test solution to that of the sample test solution.
- Identification can also be done by adding the standard solution to the sample test solution.
- Identification can also be done by adding the standard solution to the sample test solution.
Quantification and calculations
- Quantification is done by external calibration.
- Peak areas or heights are integrated and second degree calibration curve is used.
- The mass fraction of d-biotin in µg/100 g of the sample is calculated.
Remarks
- Other methods for the determination of d-biotin:
- microbiological method using Lactobacillus plantarum
- radio-assays using specific binding protein
- The method described in the standard EN 15607 can also be used for estimation of d-biocytin.
Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book.
Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
Proficiency testing schemes
Here are listed some completed, on-going and/or upcoming proficiency testing schemes concerning biotin:
Some upcoming proficiency testing schemes can be found in the EPTIS database.
Other methods available
Literature
- see separate child page below