Difference between revisions of "Vitamin K"
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
* Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book. | * Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book. | ||
| − | ** [ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/y4705e/y4705e00.pdf Greenfield H, Southgate DAT. 2003. Food composition data | + | ** [ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/y4705e/y4705e00.pdf Greenfield H, Southgate DAT. 2003. Food composition data - production, management and use. Elsevier Applied Science, London, UK.] |
* [https://metrofood-wiki.foodcase-services.com/index.php?title=Precision+data+-+vitamin+K1 link to precision data] | * [https://metrofood-wiki.foodcase-services.com/index.php?title=Precision+data+-+vitamin+K1 link to precision data] | ||
Revision as of 09:10, 23 November 2017
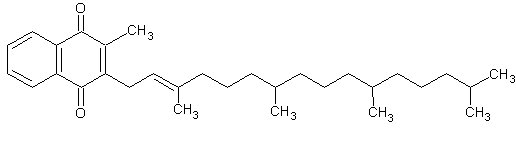
Figure 1. Phylloquinone (vitamin K1), C31H46O2, Mw = 450,70 g/mol.
Phylloquinone (vitamin K1), menaquinones (vitamin K2 group) and menadione (vitamin K3) are vitamin K active compounds. Phylloquinones can be synthesised by plants where menaquinones are synthesised only by bacteria. Instead, menadione is a synthetic form of vitamin K.
Synonyms for vitamin K:
- phylloquinone, menaquinone, menadione, naphthoquinone, antihemorrhagic factor
Contents
- 1 Golden standard
- 2 Method indicator
- 3 Scope
- 4 Principle
- 5 Key steps
- 6 Remarks
- 7 Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- 8 Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
- 9 Proficiency testing schemes
- 10 Other methods available
- 11 Literature
- 12 EuroFIR assistance to this method/guidelines
Golden standard
EN 14148:2003 Foodstuffs - Determination of vitamin K1 by HPLC
Method indicator
- Name
- Code
Scope
The European Standard EN 14148 describes a method for the determination of vitamin K1 from foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and the determination is performed by measuring the reduced phylloquinone form of vitamin K.
The method has been validated only for milk and infant formula but it has been tested to be suitable for determination of vitamin K1 also from other type of foodstuffs.
Principle
Pretreatments include removing of the fat from the sample by enzymatic treatment. Vitamin K1 is determined using HPLC with post-column reduction and fluorometric detection.
Key steps
Enzyme treatment
- Water is added and sample is homogenised prior to enzyme treatment.
- Phosphate buffer (pH 7,9-8,0) and lipase are added.
- The sample solution is incubated in 37 °C for 2 h.
Extraction
- Reagent alcohol, potassium carbonate and n-hexane are added.
- The solution is left to stand or centrifuged to get the phases separated.
- Treatments are continued with n-hexane phase by evaporating the solvent.
- The sample is redissolved in methanol.
HPLC
- Liquid chromatographic system consisting of a pump, an injector, a fluorescence detector (excitation wavelength e.g. 243 nm and emission wavelength e.g. 430 nm) and a data evaluation system.
- Reverse phase column: particle size 3-10 µm, diameter 3,0-4,6 mm, length 100-250 mm.
- Mobile phase: dichloromethane, methanol and zinc chlorideacetate solution.
- When using C18 column, cis and trans isomers of vitamin K1 elute simultaneously forming only one peak. These isomers can be separated using C30 column.
- The post-column reduction of eluate is carried out with zinc.
Identification and detection
- Vitamin K1 is detected fluorometrically (excitation wavelength 243 nm, emission wavelength 430 nm).
- Identification of vitamin K1 is done by the comparison of the retention time obtained with the standard test solution to that of the sample test solution.
- Identification can also be done by adding the standard substance to the sample test solution.
Quantification and calculations
- Peak areas or heights obtained with sample solutions are compared to the corresponding values of the standard substance to quantify vitamin K1 by external calibration.
- It should be noted that the vitamin K1 concentration in the final sample solution is very low, thus it is important to prevent possible contamination.
Remarks
- Vitamin K is sensitive to light, thus unnecessary exposure to light should be avoided.
- The concentration of calibration solution should be checked spectrometrically because of the differences in the purity of the standard substances.
- A blank sample should be prepared using same treatments than when preparing samples to exclude the possibility of contamination.
- The standard describes also alternative HPLC conditions.
Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book.
Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
Proficiency testing schemes
Here are listed some completed, on-going and/or upcoming proficiency testing schemes concerning vitamin K:
Some upcoming proficiency testing schemes can be found in the EPTIS database.
Other methods available
- AOAC 974.30 Menadione sodium bisulfite (water-soluble vitamin K3) in feed premixes
- gas chromatographic
- AOAC 992.27 trans Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) in ready-to-feed, milk-based, infant formula
- liquid chromatographic
- AOAC 999.15 Vitamin K in milk and infant formula
- liquid chromatographic
Literature
- see separate child page below