Difference between revisions of "Vitamin E"
m (6 revisions imported) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<br /> Figure 1. Structures of tocopherols. | <br /> Figure 1. Structures of tocopherols. | ||
| − | + | α-tocopherol: C<sub>29</sub>H<sub>50</sub>O<sub>2</sub>, Mw = 430,71 g/mol. | |
| − | The group vitamin E includes eight compounds that have similar biological activity as | + | The group vitamin E includes eight compounds that have similar biological activity as α-tocopherol. These compounds are α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols and the corresponding tocotrienols. The measurement of vitamin E is carried out by determination of tocopherols, and vitamin E activity can be calculated taking the activity of each tocopherol into account. |
Note: | Note: | ||
| − | USDA Food Composition Database for Standard Reference, Release 25 defines vitamin E as | + | USDA Food Composition Database for Standard Reference, Release 25 defines vitamin E as α-tocopherol only ) . This definition has been adopted by many European food databases. |
Synonyms for vitamin E: | Synonyms for vitamin E: | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
=== Golden standard === | === Golden standard === | ||
| − | * [http://www.cen.eu/cen/Sectors/TechnicalCommitteesWorkshops/CENTechnicalCommittees/Pages/Standards.aspx?param=6256&title=CEN/TC%20275 EN 12822:2000]Foodstuffs - Determination of vitamin E by high performance liquid chromatography - Measurement of | + | * [http://www.cen.eu/cen/Sectors/TechnicalCommitteesWorkshops/CENTechnicalCommittees/Pages/Standards.aspx?param=6256&title=CEN/TC%20275 EN 12822:2000]Foodstuffs - Determination of vitamin E by high performance liquid chromatography - Measurement of α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols. |
** draft prEN 12822:2012 | ** draft prEN 12822:2012 | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
=== Scope === | === Scope === | ||
| − | The European Standard EN 12822 describes a method for the determination of vitamin E in foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Vitamin E content is determined by measurement of | + | The European Standard EN 12822 describes a method for the determination of vitamin E in foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Vitamin E content is determined by measurement of α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols. |
=== Principle === | === Principle === | ||
| − | Sample treatments usually include saponification and extraction. | + | Sample treatments usually include saponification and extraction. α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols are determined by HPLC using fluorometric detection. Also photometric detection (UV-range) can be used but fluorometric detection is preferred. |
=== Key steps === | === Key steps === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* Mobile phase: e.g. 3 % 1,4-dioxane in n-hexane. | * Mobile phase: e.g. 3 % 1,4-dioxane in n-hexane. | ||
* Also other chromatographic systems can be used if equivalent results are guaranteed. | * Also other chromatographic systems can be used if equivalent results are guaranteed. | ||
| − | ** Reverse phase columns can be used to quantify | + | ** Reverse phase columns can be used to quantify α- and δ-tocopherols, but β- and γ-tocopherols cannot be separated. |
* The performance criteria is the baseline separation of the analytes from interferences. | * The performance criteria is the baseline separation of the analytes from interferences. | ||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
** Peak areas or peak heights of the samples are compared to the corresponding values for the standard substances. | ** Peak areas or peak heights of the samples are compared to the corresponding values for the standard substances. | ||
* The linearity of the calibration must be checked. | * The linearity of the calibration must be checked. | ||
| − | * The mass fraction of | + | * The mass fraction of α-, β-, γ- or δ-tocopherol is calculated and result is reported as mg/100 g of the sample. |
* For calculation of vitamin E content, biological activities must be taken into account. | * For calculation of vitamin E content, biological activities must be taken into account. | ||
| Line 105: | Line 105: | ||
* Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book. | * Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book. | ||
| − | ** [ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/y4705e/y4705e00.pdf Greenfield H, Southgate DAT. 2003. Food composition data | + | ** [ftp://ftp.fao.org/docrep/fao/008/y4705e/y4705e00.pdf Greenfield H, Southgate DAT. 2003. Food composition data - production, management and use. Elsevier Applied Science, London, UK.] |
* [https://metrofood-wiki.foodcase-services.com/index.php?title=Precision+data+-+vitamin+E link to precision data] | * [https://metrofood-wiki.foodcase-services.com/index.php?title=Precision+data+-+vitamin+E link to precision data] | ||
| Line 128: | Line 128: | ||
* [http://methods.aaccnet.org/summaries/86-06-01.aspx AACC 86-06.01] Analysis of Vitamins A and E by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | * [http://methods.aaccnet.org/summaries/86-06-01.aspx AACC 86-06.01] Analysis of Vitamins A and E by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography | ||
| − | * AOAC 948.26 | + | * AOAC 948.26 α-Tocopheryl acetate (supplemental) in foods and feeds |
** colorimetric | ** colorimetric | ||
| − | * [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/971_30.pdf AOAC 971.30] | + | * [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/971_30.pdf AOAC 971.30]α-Tocopherol and α-tocopheryl acetate in foods and feeds |
** colorimetric | ** colorimetric | ||
* [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/975_43.pdf AOAC 975.43]Identification of RRR- or all-rac-alpha-tocopherol in drugs and food or feed supplements | * [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/975_43.pdf AOAC 975.43]Identification of RRR- or all-rac-alpha-tocopherol in drugs and food or feed supplements | ||
| Line 136: | Line 136: | ||
* AOAC 988.14 Tocopherol isomers in mixed tocopherols concentrate (FCC, USP, AOAC method) | * AOAC 988.14 Tocopherol isomers in mixed tocopherols concentrate (FCC, USP, AOAC method) | ||
** gas chromatographic | ** gas chromatographic | ||
| − | * [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/989_09.pdf AOAC 989.09] | + | * [http://www.aoac.org/omarev1/989_09.pdf AOAC 989.09]α-Tocopheryl acetate in supplemental vitamin E concentrates |
** gas chromatographic | ** gas chromatographic | ||
| − | * AOAC 992.03 Vitamin E activity (all-rac- | + | * AOAC 992.03 Vitamin E activity (all-rac-α-tocopherol) in milk-based infant formula |
** liquid chromatographic | ** liquid chromatographic | ||
Latest revision as of 13:33, 9 May 2019
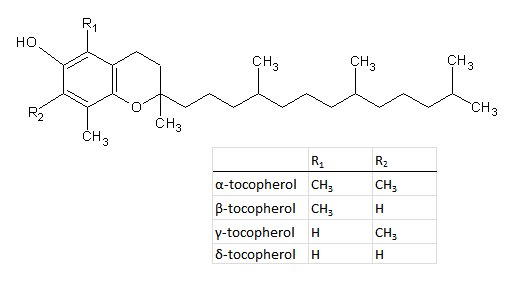
Figure 1. Structures of tocopherols.
α-tocopherol: C29H50O2, Mw = 430,71 g/mol.
The group vitamin E includes eight compounds that have similar biological activity as α-tocopherol. These compounds are α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols and the corresponding tocotrienols. The measurement of vitamin E is carried out by determination of tocopherols, and vitamin E activity can be calculated taking the activity of each tocopherol into account.
Note:
USDA Food Composition Database for Standard Reference, Release 25 defines vitamin E as α-tocopherol only ) . This definition has been adopted by many European food databases.
Synonyms for vitamin E:
- tocopherol, ephanyl
Contents
- 1 Golden standard
- 2 Method indicator
- 3 Scope
- 4 Principle
- 5 Key steps
- 6 Remarks
- 7 Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- 8 Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
- 9 Proficiency testing schemes
- 10 Other methods available
- 11 Literature
- 12 EuroFIR assistance to this method/guidelines
Golden standard
- EN 12822:2000Foodstuffs - Determination of vitamin E by high performance liquid chromatography - Measurement of α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols.
- draft prEN 12822:2012
Method indicator
- Name
- Code
Scope
The European Standard EN 12822 describes a method for the determination of vitamin E in foodstuffs by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Vitamin E content is determined by measurement of α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols.
Principle
Sample treatments usually include saponification and extraction. α-, β-, γ- and δ-tocopherols are determined by HPLC using fluorometric detection. Also photometric detection (UV-range) can be used but fluorometric detection is preferred.
Key steps
General
- The sample treatments described below are meant for other samples than oil and fat samples (low water content) containing unesterified tocopherols.
- For oil and fat samples with unesterified tocopherols, the following pretreatments are used:
- n-hexane is added to dissolve the test portion.
- Solution is diluted prior to chromatography.
- Only normal phase chromatography should be used for determination of tocopherols in these oil and fat samples.
Saponification
- The sample is homogenised prior to saponification.
- Ethanol or methanol, water, an antioxidant and an aqueous potassium hydroxide are added.
- Saponification includes heat treatment.
- 80-100 °C, 15-40 min
Extraction
- The ratio of alcohol to water should be 1:1 before extraction to avoid emulsions.
- Extraction is carried out using suitable solvent.
- Recovery should be checked to exclude the possibility of losses.
- The extract is washed with water.
- Solvent is evaporated and sample is redissolved using e.g. mobile phase.
HPLC
- Liquid chromatographic system consisting of a pump, an injector, a fluorescence detector (excitation wavelength 295 nm and emission wavelength 330 nm) and data evaluation system.
- Also UV detector (292 nm) may be used.
- Normal phase column: particle size 5 µm (silica phase), diameter e.g. 4,0-4,6 mm, length 100-250 mm.
- Mobile phase: e.g. 3 % 1,4-dioxane in n-hexane.
- Also other chromatographic systems can be used if equivalent results are guaranteed.
- Reverse phase columns can be used to quantify α- and δ-tocopherols, but β- and γ-tocopherols cannot be separated.
- The performance criteria is the baseline separation of the analytes from interferences.
Identification and detection
- Tocopherols are detected fluorometrically (excitation wavelength 295 nm and emission wavelength 330 nm) or using UV detector (292 nm).
- Identification of tocopherols is done by the comparison of the retention time obtained with the standard test solution to that of the sample test solution.
- Identification can also be done by adding a small amount of the appropriate standard solution to the sample test solution.
Quantification and calculations
- External standard method is used for quantification.
- Peak areas or peak heights of the samples are compared to the corresponding values for the standard substances.
- The linearity of the calibration must be checked.
- The mass fraction of α-, β-, γ- or δ-tocopherol is calculated and result is reported as mg/100 g of the sample.
- For calculation of vitamin E content, biological activities must be taken into account.
Remarks
- The purity of standard substances can vary, thus it is necessary to check the concentration of calibration solution spectrometrically.
- Unnecessary exposure to light must be avoided during analysis.
- Alternative HPLC conditions are described in the Standard.
- Oldet methods
- colorimetric
- gives a total tocopherol content
- forming complexes unstable
- GLC
- colorimetric
Criteria for analytical performance and analytical quality control
- Greenfield and Southgate discuss the criteria for analytical performance and quality of analytical data in their book.
Certified Reference Materials/Standard Reference Material
Proficiency testing schemes
Here are listed some completed, on-going and/or upcoming proficiency testing schemes concerning vitamin E:
DGF - Deutsche Gesellschaft für Fettwissenschaft
Some upcoming proficiency testing schemes can be found in the EPTIS database.
Other methods available
- AACC 86-06.01 Analysis of Vitamins A and E by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography
- AOAC 948.26 α-Tocopheryl acetate (supplemental) in foods and feeds
- colorimetric
- AOAC 971.30α-Tocopherol and α-tocopheryl acetate in foods and feeds
- colorimetric
- AOAC 975.43Identification of RRR- or all-rac-alpha-tocopherol in drugs and food or feed supplements
- polarimetric
- AOAC 988.14 Tocopherol isomers in mixed tocopherols concentrate (FCC, USP, AOAC method)
- gas chromatographic
- AOAC 989.09α-Tocopheryl acetate in supplemental vitamin E concentrates
- gas chromatographic
- AOAC 992.03 Vitamin E activity (all-rac-α-tocopherol) in milk-based infant formula
- liquid chromatographic
Literature
- see separate child page below